There are certain terms that you will see frequently when you are learning how to trade forex – such as pips, lots, and orders. We measure the movement of a pair’s price in pips, the lot size shows the units of currency being traded, and we need to place orders to access the markets.
Our Forex Signals
1 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
3 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
 Most popular
Most popular
6 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
Lifetime
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratioSeparate Swing Trading Group
 Up to 3 signals weekly
Up to 3 signals weekly 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
1 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiotime
As such, in part 3 of this beginners forex course, we explain the ins and outs of pips, lots, and orders.
It is crucial that you grasp every aspect of this before diving in. With that in mind, we also include examples, how to read your next forex quote, and various order types. We also list what to look out for in a broker – to facilitate your entry into this ultra liquid marketplace.
Learn 2 Trade Forex Course - Master Your Forex Trading Skills Today!

- 11 core chapters will teach you everything you need to know about forex trading
- Learn about forex trading strategies, technical and fundamental analysis, and more
- Designed by seasoned forex traders with decades of experience in the space
- Exclusive all-in price of just £99

Forex Trading Basics: Pips, Lots & Orders
Although this is a trading basic, ‘pips’ and ‘lots’ particularly can appear challenging for newbies. As we mentioned, you will see these terms used frequently when trading currencies.
As such, it’s a good idea to get your head around what they are and how they affect your trading endeavours. Throughout this beginners forex course, we discuss all the important metrics you need to have a grasp of.
What are Pips in Forex?
We illustrate the minimum price movements in ‘pips’ (percentage in point) in the forex markets. Each element of the price you are quoted on an FX pair will represent a pip. This shows the smallest amount that a market can move in value.
See a simple example below using 4 decimal places:
- If GBP/USD shifts from £1.4128 to £1.4129
- This shows us a movement of 1 pip
Pips allow you to calculate your unrealized gains and losses accurately, without using the monetary value (e.g. pounds or dollars). This is effective for gauging success. For example, although trader A might have a balance of $100 and trader B has $1,000 – if both make gains of 3 pips – they have been just as fortunate or skilled. This is in the sense that they both successfully made 3 pips.
What are Lots in Forex?
By this point, we have established what pips are, and that this indicates the smallest amount a currency pair can rise or fall. On the other hand, a ‘lot’ refers to the minimum quantity of units of the base currency you can trade via that particular broker.
As such, you will frequently see the term ‘minimum lot’ or ‘minimum position’ – stipulating what kind of account you can access. Some trading platforms will only be able to offer standard lots.
The best forex brokers will offer you more than just this option when trading currencies. This can include mini, micro, and maybe even nano lots.
- A standard lot = 100,000 currency units: If you are trading this size lot and the pair moves 1 pip – this would be the equivalent of a $10 shift.
- A mini lot = 10,000 currency units: This is parallel to one-tenth of a standard lot – 1 pip is $1.
- A micro lot = 1,000 currency units: This equates to one-tenth of a mini lot – 1 pip equals $0.10
- A nano lot = 100 currency units: This is the equivalent of one-tenth of a micro lot(or a hundredth of a mini lot) – 1 pip equates to $0.01
This is important as it will help you with position sizing – determining how large your trade should be, based on how much you have in your account. If you need to have a practice run and try out different position sizes, the best forex simulators enable you to use fractional lot demo accounts. Crucially, using risk-free paper trading funds.
Many platforms support micro-lots, where 1 pip is only 100 units, and will automatically provide you with a free demo account where you can test this out.
What are Orders in Forex?
An ‘order’ when forex trading refers to you how you enter and exit the currency markets. It entails you giving your chosen brokerage a set of specific instructions – regarding your prediction on the direction of the FX pair you are trading. The platform then executes your position for you.
- Market – AUD/USD
- Entry – buy or sell?
- Amount – how much would you like to allocate to this position?
- Leverage – do you want to boost your stake with leverage?
- Stop-loss – would you like to specify your exit level to control your losses?
- Take-profit – do you wish to exit this trade when you have made a specific profit of say 4%?
We talk about all elements of forex trading orders in more detail shortly, but for further clarification:
- Let’s imagine you are trading EUR/AUD
- The broker quotes a buy price of AU$1.5785 and a sell of AU$1.5779
- You need to decide whether you think this pair is more likely to see a rise or fall in value
- If you think the value of EUR/AUD will rise – place a buy order
- Alternatively, if you believe this value will fall – place a sell order
- Add the most suitable leverage, if you wish
If you need a recap on leverage, we cover this subject in part 2 of this beginners course – forex trading basics: margin and leverage.
How to Interpret a Forex Quote
The first thing to mention is that the quote you see when changing money for a vacation and the one you see when trading will appear different.
For instance, if you google GBP/USD, you will see something like this – ‘1 British pound equals £1.41’. This means that for every 1 GBP, the markets will give you 1.41 in US dollars.
However, throughout this course so far, we have used longer example quotes. This is because when you are seeking a quotation from your online broker, you will see a figure with 4 or 5 decimal places. For instance, £1.41 might instead be shown as £1.4128 or £1.41285. This enables online trading platforms to illustrate the smallest price shift possible.
See below an example of how pips are calculated, with a 5 digit quotation:
- $1.23456
- 1 equals 10,000 pips
- 2 equals 2,000 pips
- 3 equals 300 pips
- 4 equals 40 pips
- 5 equals 5 pips
- 6 equals 0.6 pips or 6 pipettes
As you can see, the 5th decimal place is actually fractionalized, so we are able to see market fluctuations of less than 1 pip. Fractional forex trades are becoming more and more popular at modern brokerages.
Forex Quote Examples
See an example below to shed some more light on the subject:
- Let’s say you are trading USD/CAD, priced at $1.2465
- Every 1 US dollar equates to 1.2465 Canadian dollars
- Here, the fourth decimal place equals 1 pip
- As such, if USD/CAD falls from $1.2465 to $1.2463 – this is a decrease in value of 2 pips
Now, let’s see an example scenario where the Japanese yen is included. Notice that 1 pip is in second place after the decimal – instead of the fourth. This is always the case where JPY is included, although some brokers price JPY with 3 digits after the decimal point.
Below you will see an example of both:
- AUD/JPY has shifted from ¥85.34 to ¥85.37 – this shows an upward movement of 3 pips
- CAD/JPY has moved from ¥90.405 to ¥90.401 – this shows a 0.4 pip, (or 4 pipettes) decline in value
You also need to take into account the spread, which we talk about next. Also, for those who have never traded in any capacity – you will see a breakdown of forex order types and how to use them shortly.
Forex Broker Spread in Pips
Every online broker charges a small fee called a ‘spread’ to enter the currency markets. This is quite simply the difference between the buy (bid) and sell (ask) rate – and it essentially ensures a profit for the provider. This is especially the case for low or no commission platforms like Capital.com or AvaTrade.
Eightcap - Regulated Platform With Tight Spreads

- Minimum deposit of just 250 USD to get lifetime access to all the VIP channels
- Use our Secure and Encrypted Infrastructure
- Spreads from 0.0 pips on Raw Accounts
- Trade on the Award-Winning MT4 & MT5 Platforms
- Multi-jurisdictional Regulation
- No Commission Trading on Standard Accounts

These forex brokers charge hardly any fees, so need to keep the wheels turning by charging a spread. The trading platform in question provides you with access to the currency markets and handles the end-to-end transaction for you. This is a necessary part of forex trading, so ensure you look for platforms with a tight spread.
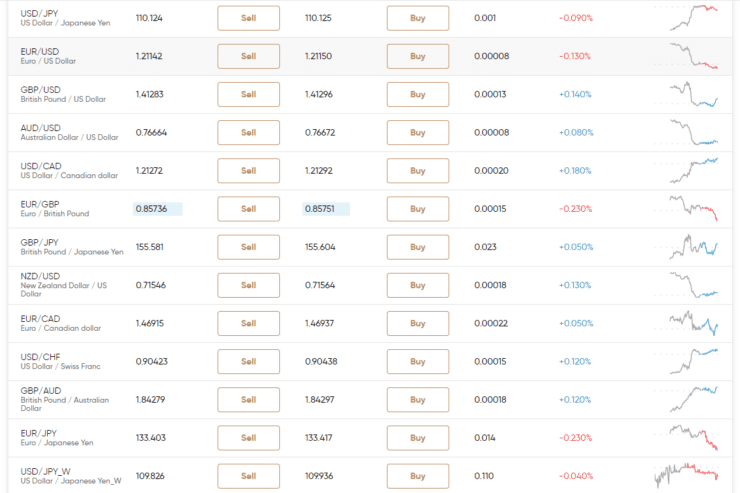
See a range of examples below including 2, 3, 4, and 5 decimal place forex quotes to show you pips on each:
- 2 decimal places: AUD/JPY – buy ¥84.58 and sell ¥84.56 = 2 pip spread
- 3 decimal places: CHF/JPY – buy ¥121.638 and sell ¥121.633 = 0.5 pips (5 pipettes) spread
- 4 decimal places: GBP/USD – buy $1.4135 and sell $1.4134 = 1 pip spread
- 5 decimal places: USD/ZAR – buy R 13.78333 and sell R 13.77433 = 90 pips spread
- 5 decimal places: EUR/CAD – buy CA$1.47642 and sell CA$1.47648 = 0.6 pips (6 pipettes) spread
Whatever the spread is at your chosen brokerage is the amount you will start your trade in the red. As we said, this is a fee.
How to Calculate the Value of Forex Pips Yourself
As well as understanding forex quotations at your chosen trading platform, it’s crucial that you understand how to work out your gains and losses in pips.
You will see below how you can calculate the value of a pip:
- One Pip is the equivalent of 0.0001
- The account base currency is euros
- The pair traded is EUR/USD
- The exchange rate of the pair is 1.22094
- A standard lot is 100,0000 euros
- Pip Value = 0.0001/1.22094 x 10,0000
- In this scenario, using a standard lot, each pip is worth €8.19
You can easily calculate this yourself by dividing the pip value by the quoted price (exchange rate) and then multiplying this by the aforementioned lot size.
Forex Trading Order Types
We’ve already explained what forex trading orders are, so now we can offer some more detail on what each does, and how you can use them yourself.
Long or Short Orders: Buy and Sell
No matter which broker turns out to be the most suitable choice for you and your forex trading system, you will need to make a choice between a ‘buy’ and ‘sell’ order. These orders indicate what your prediction is – which determines whether you are ‘long’ or ‘short’ on your chosen pair.
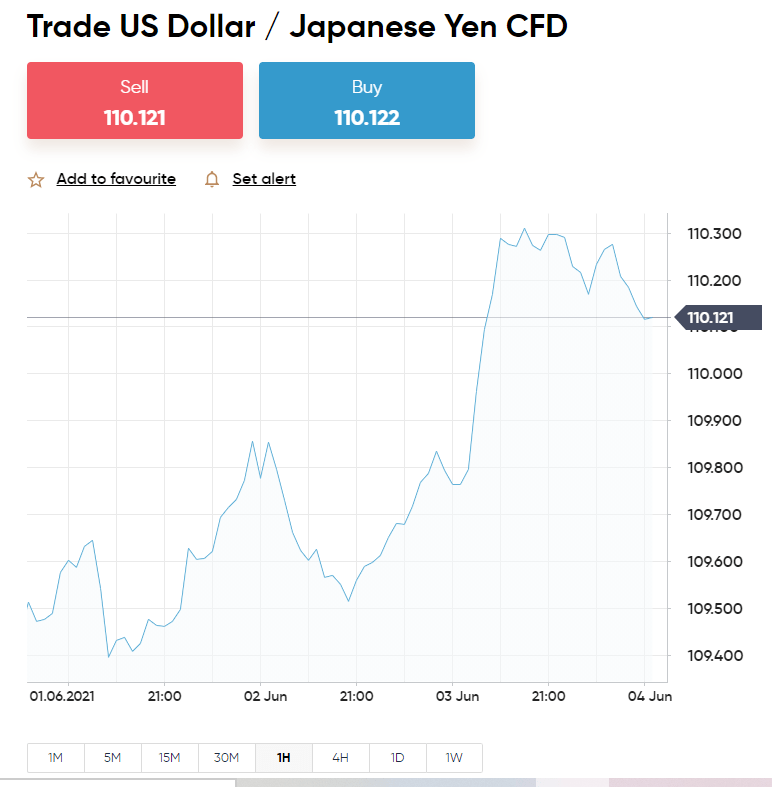
As we said, if you believe the marketplace has undervalued the forex pair you are trading, meaning it will probably see a price increase – you can ‘go long’ by creating a buy order.
Please note that if you go short on a currency pair, you will need to close the position with a buy order – because you entered it with a sell order. If entering with a buy order, you close it with a sell order.
Entry Orders: Market and Limit
After buy and sell orders – ‘market’ and ‘limit’ orders illustrate your preferred way to enter the currency trade.
Market Order
A market order is instantaneous and allows you to get your hands on the current or next nearest price.
Let’s clear things up with an example of when you might place a market order:
- You are trading New Zealand dollars against US dollars, priced at NZ $0.72451
- After performing some technical analysis on NZD/USD you think this is a great price
- As such, you place a market order and the broker executes this straight away
- You enter the market at NZ $0.72453
As you can see, in this scenario, you placed a market order at NZ $0.72451, but when the order went through, it priced the pair at NZ $0.72453. In this instance, NZD/USD fell by 0.2 pips. This is unavoidable due to price fluctuations experienced in the currency markets – otherwise known as ‘slippage’.
Limit Order
A limit order comes into play when you don’t like the current price of the asset you want to trade and would prefer to wait until it reaches a more desirable price.
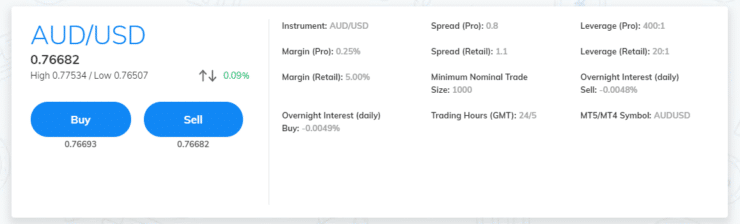
- You are interested in the pair AUD/USD
- This market is currently valued at $0.7757
- You do not wish to enter this trade until the pair rises by 3%
- As such, you will set your limit order to 3% above the current price, which is $0.7989
- When, or if AUD/USD hits $0.7989 – the trading platform will action your order immediately
- This ensures you enter the market at your desired price and not before
Unless you are happy with the pair’s current value – you don’t need to worry about timing the markets. This is because the broker will execute your limit order automatically as soon as the pair hits that price point.
Automated Orders: Stop-Loss and Take-Profit
We’ve covered the forex trading basics of what pips, lots, and orders are. We’ve also talked about how you can enter the currency markets in a price-specific way. The same is possible when it comes to planning your exit from a position.
Stop-Loss
Starting with ‘stop-loss order’, this simply means you can instruct your chosen trading platform to stop your losses automatically, at a price specified by you.
Eightcap - Regulated Platform With Tight Spreads

- Minimum deposit of just 250 USD to get lifetime access to all the VIP channels
- Use our Secure and Encrypted Infrastructure
- Spreads from 0.0 pips on Raw Accounts
- Trade on the Award-Winning MT4 & MT5 Platforms
- Multi-jurisdictional Regulation
- No Commission Trading on Standard Accounts

Let’s clear the mist with a realistic example:
- You are still trading AUD/USD, which is priced at $0.7757 and you are long
- Let’s say you are working on a risk/reward of 1:4 meaning for every 1% risk on a trade, you hope for a reward of 4%
- This means you are not willing to lose more than 1% on this position
- As such, you set your stop-loss order to $0.7679 – which is 1% lower than the current price of the pair
- If the market falls to this specific value – your trade will be closed by the broker
As you can see, it couldn’t be easier to stop your losses from spiralling out of control when trading in this liquid yet volatile marketplace!
Take Profit
A ‘take profit’ order needs very little explanation, as it works very similarly to the previously talked about stop-loss order – only with the reverse effect.
See an example below, still working on the risk/reward ratio of 1:4:
- You are trading AUD/USD and are sticking with a market order of $0.7757
- You are long on the pair – so placed your stop-loss order at 1% lower than the entry price
- As such, you need to set the take-profit order to $0.8067, which is 4% higher
- If AUD/USD rises by 4% to $0.8067, the take-profit order is actioned – locking in your gains
- If the pair falls by 1% to $0.7679, the stop-loss order is executed – stopping your losses
Please note that if you are short on your chosen FX pair, the stop loss will be above the entry and the take-profit will be below. The order that is actioned will depend on which price point is reached first. The obvious goal is to be correct and have this lock in your gains.
How to Choose a Forex Broker to Place Orders
Part 3 of this course has covered everything there is to know about pips, lots, and orders. As we mentioned, for you to access this popular market and place orders, you will need to sign up with a trading platform that fits the bill.
See below a list of key considerations when searching for the best trading platform to suit your goals.
Platform Regulatory Standing
Regulatory standing is very important when looking for a reliable brokerage. Financial regulators are very picky about who they give licenses to. The platforms must provide thorough audits, adhere to KYC rules, apply leverage restrictions, and more.
One of the most important differences between a regulated broker and one that isn’t is that the former will have to keep your money in a separate tier-1 bank account from its own. The biggest bodies in the space are the FCA, ASIC, FINRA, and CySEC, to name a few.
Forex Market Availability
Checking out what forex markets will be available to you is essential when looking for a good platform. Some might only be able to offer popular major currencies like US dollars and euros. Whilst such pairs come with tighter spreads, there will be a time when a little more volatility is required. This might also depend on your strategy.
There are some regulated and respected brokers out there such as Capital.com and AvaTrade that also provide access to emerging markets. This includes the likes of the Mexican peso, Swedish krona, Israeli new shekel, Norwegian krone, Turkish lira, South African rand, Russian ruble, and Chilean peso.
Low Fees and Spreads
No two brokers are the same, so it’s worth mentioning that commissions and spreads are something you will need to check at every platform you look at.
Fees we commonly see charged by forex brokers are as follows:
- Spread: As discussed, this is the gap between the buy and the sell price of your chosen market. The amount you pay will vary between platforms so always check that this is competitive before signing up. The smaller the spread the better it will be for your gains.
- Commission Fees: This is another fee that can vary by a mile. You might see that one broker charges a fixed rate of say 3% on each trade. This means if you enter the market with a $50 order, you have to pay $1.50. If your trade is worth $100 upon closing you would pay $3. There are, however, many brokers that charge 0% commission.
Something else to look out for is inactivity fees. Some brokers will charge this after a specified time of say one year. The amount will vary but can be as much as $20 per month.
Minimum Forex Lot Size
Consider the aforementioned lot size when choosing a platform. Some providers only accept standard lot sizes, which leaves you having to put up more trading capital than you expected.
- Tip: Look for online brokers that can offer more than one lot/position size – such as nano, micro, or mini.
You can access the aforementioned micro, mini and standard accounts at top-rated platforms Capital.com and AvaTrade. Note that some brokers refer to this as ‘units’ so may just say – ‘minimum position 100,000 units’ which would be a standard lot.
Accepted Deposit Types
Remember, you can’t place an order without having some money in your trading account. A such, it’s important to consider what your preferred payment type is and what the trading platform accepts.
Many online brokers now will allow you to deposit funds using a variety of different methods, covering bank transfers and credit/debit cards like Visa, Visa Electron, and Mastercard. You may also want to make sure your chosen provider accepts e-wallets.
Trading Platform Features
Some of the most useful features to learn pips, lots and orders are as follows:
- Copy Trader
- Forex EAs
- Portfolio simulators
What features you need from a trading platform will depend on your strategy. If you don’t have one yet – you will find everything you need to know in part 9 of this course.
How to Place a Forex Order With a Broker: 5 Simple Steps
Now that you have a full comprehension of forex pips, lots and orders, you will need to know how to place one with a reputable brokerage.
See below for a run-through of how to get started, once you have finished this beginners forex course.
- Step 1 – Sign up With a Broker: The first step is to sign up with a respected broker who can provide you with access to the currency markets. We have mentioned a few throughout this course that are worth your consideration.
- Step 2 – Provide Identification: All regulated brokers follow KYC rules. As such, you will need to send a copy of your passport/driver’s license and a bank statement or utility bill to validate who you are.
- Step 3 – Fund Your Account: Select your preferred payment method from what the broker accepts. Importantly, check everything before confirming your deposit.
- Step 5 – Find a Forex Market: Next, you can find a market to trade. We talk about the various pair types in part 6 of this course.
- Step 6 – Place Your Order: Place your order including; your chosen lot size (or the number of units), buy or sell (long or short), and a market or limit. Finally, enter the stop-loss, and take profit value to stop your losses and lock in your gains. As we said, you can use your risk/reward ratio to gauge this. Common ones are 1:2, 1:3, and 1:4.
Just a recap, when you see minimum ‘lot’ or ‘units’ when placing an order – this refers to the lowest number of currency units that you can buy or sell at that particular brokerage.
Pips, Lots & Orders: To Conclude
By this stage, you should now have a grasp of the importance of pips, lots, and orders. Of course, the order we place dictates what position we take in the currency markets. That could be long or short, or perhaps inclusive of a limit order to help you be price specific when entering the trade.
Pips help us calculate our gains and losses when trading forex. This is also a universal way to gauge where to put a stop-loss and take profit on every trade.
Many years ago the only position size available was standard lots, albeit, many brokers can now offer micro and mini lots. This means that you are able to open a fractional trade of up to a hundredth the size of a standard lot – which is perfect for beginners.
Learn 2 Trade Forex Course - Master Your Forex Trading Skills Today!

- 11 core chapters will teach you everything you need to know about forex trading
- Learn about forex trading strategies, technical and fundamental analysis, and more
- Designed by seasoned forex traders with decades of experience in the space
- Exclusive all-in price of just £99

FAQs
What are pips in forex trading?
How many lots would I be able to trade with $10,000
How is the pip value calculated when forex trading?
How much is 0.01 lots in forex trading?
How do I use pips and lots to calculate my gains and losses?