CFD Trading in the online investment space is jam-packed with financial terms that to the untrained eye – can appear somewhat confusing. At the forefront of this is the multi-trillion pound CFD space.
Our Forex Signals
1 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
3 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
 Most popular
Most popular
6 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
Lifetime
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratioSeparate Swing Trading Group
 Up to 3 signals weekly
Up to 3 signals weekly 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
1 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiotime
In its most basic form, CFDs allow you to invest in an asset without actually owning it. Instead, you are simply speculating on the asset’s future price.
Fancy finding out what CFDs are and why you might decide to include them in your long-term investment goals? If so, be sure to read our comprehensive CFD Trading Guide. Within it, we cover the ins and outs of what CFDs are, how they work, what they allow you to trade, and more.
What are the Pros and Cons of Trading CFDs?
The Pros The Cons
What is a CFD? Simple CFD Meaning
A contract-for-difference, or simply a ‘CFD’, is a financial instrument that allows you to trade an asset, or group of assets, without needing to own it. Instead, you are merely speculating on whether you think the price of the asset will go up or down. CFDs are a highly useful trading instrument, not least because they can represent virtually any asset class.
For example, let’s say that you wanted to trade gold. In the traditional sense, it would be a logistical nightmare to physically purchase and store gold with the view of making a profit. This is also the case with other hard assets like oil and natural gas. With that said, the CFD space covers thousands of assets.

Whether its stocks and shares, ETFs, futures, options, cryptocurrencies, energies, interest rates, or indices – you’ll find a CFD. Although you don’t own the underlying asset per-say, CFDs allow you to trade the asset in much the same way.
For example, let’s say that you wanted to invest in the S&P 500. For those unaware, the S&P 500 is a stock market index that tracks the 500 largest companies listed on the NYSE and NASDAQ. Instead of needing to purchase 500 shares individually, you could buy a single CFD. Depending on which way the markets go, you would make a profit or loss as the price of the S&P 500 moves.
How do CFDs work?
CFDs are actually quite simple to trade once you know what you are doing. The reason for this is that CFDs operate largely like any other tradable instrument. In other words, once you decide which way you think your chosen asset will move in the markets, you simply need to place a trade and determine where your exit point is.
With that being said, it’s probably best that we give you a couple of examples to clear the mist.
CFD Trading Example 1: Going Long on HSBC Shares
Let’s say that you believe the price of HSBC shares is due to an increase in the short-term. As you’re only looking to place a short-term trade, it wouldn’t make sense to purchase the shares in the traditional sense. In doing so, you’d get hit with huge fees that would likely make the trade unviable. Instead, you decide to purchase HSBC shares in the form of a CFD.
- You buy 10 x CFDs in HSBC at £5 per share
- Your total trade size is £50 (10 x £5)
- Later that day, the price of HSBC increases to £6 per share
- You decide to sell your CFDs, which you can do at the click of a button
- As you sold the CFDs for £1 more than what you paid (£6 – £5), you made a total profit of £10 (you had 10 shares)
Crucially, you were able to make a profit on the future price of HSBC without actually owning the shares. Instead, you simply engaged in CFD trading.
CFD Trading Example 2: Going Short on Oil
In this example, you decide that you want to ‘short’ oil. This means that you believe the price of oil will go down. Shorting is one of the most attractive aspects to CFDs, as they allow you to profit even when the markets are down. The short-selling process works largely the same as the above example on going long, albeit, in reverse.
- You sell 20x CFDs in oil at $70 per barrel
- This means that your total trade size is $1,400 (20 x $70)
- Later that day, the price of oil goes down to $60 per barrel due to surplus production volumes in Saudi Arabia
- As such, you’re currently looking at a profit of $10 per barrel
- You have 20 x CFDs, so that’s $200 in profit
- In order to realize your profits, you would be required to buy the CFDs back, as you initially placed a short order
As you can see from the above example, short-selling in the CFD space is just as straightforward as going long.
What CFD Markets can I Trade?
In a nutshell, if you can trade an asset in the traditional financial markets, then you can be all-but-certain that a CFD exists. The overarching reason for this is that CFDs merely track the real-world price of an asset. For example, if the price of gold goes up by 3% in the global marketplace, a gold CFD will also rise by 3%.
Nevertheless, we’ve listed some of the most popular CFD asset classes below.
✔️ Stocks and Shares
✔️ Indices
✔️ Interest Rates
✔️ Hard Metals
✔️ Energies
✔️ Futures
✔️ Options
✔️ Cryptocurrencies
CFD Trading Fees
In order to engage in CFD trading, you will need to use an online broker. Although we’ll cover the ins and outs of how to choose a CFD broker later in our guide, it is important to explore what trading fees you need to be made aware of.
🥇 Commission
First and foremost, CFD brokers are in the business of making money. As such, you might need to pay a trading commission every time you buy and sell a CFD. If you do, then it’s likely to be charged as a percentage of the amount you trade.
For example, let’s say that you buy £1,000 worth of CFDs, and the broker charges 1%. This means that you’ll need to pay a commission of £10. Moreover, you’ll also need to pay a commission when you decide to sell your CFDs. As such, were you to sell the same CFDs when they were worth £1,500, you’d pay £15 in commission.
🥇 Spreads
Newbie traders often overlook the spread – especially when using a broker that claims to offer fee-free trading. However, the spread is a trading fee that you will pay indirectly. In its most basic form, the spread is the difference between the ‘buy’ price and the ‘sell’ price.
For example, let’s say that you’re looking to trade natural gas. If the buy price was $51, and the selling price was $50, this indicates a spread of 2%. Therefore, you would need to see your trade increase in value by at least 2% just to break even. This is why you need to choose a CFD broker that offers super-tight spreads.
🥇 Overnight Financing
You also need to make some considerations on overnight financing if you plan to trade CFDs on leverage. Put simply, when you buy or sell a CFD on leverage, you are effectively borrowing funds from the broker in question. This is because the broker is allowing you to trade with more money than you have in your account.
As such, overnight financing on CFDs works largely the same way as a loan. You will pay a small percentage of interest, which is charged for as long as you keep the position open for more than 24 hours. As leverage plays such a large role in the CFD industry, we’ll explain how it works in the next section.
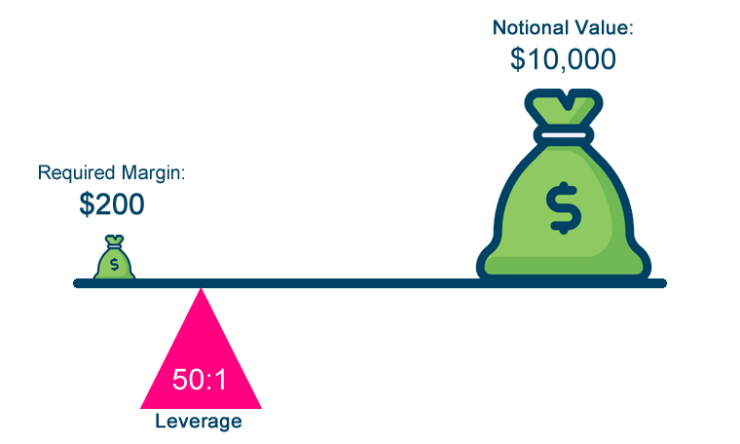
How Does CFD Leverage Work?
For those of you with a higher appetite for risk, leverage allows you to trade more than what you have available in your brokerage account. On the one hand, this allows you to amplify your profits if you feel confident about a particular trade. However, leverage is an extremely high-risk trading tool, as you can equally amplify your losses.
When using leverage on your trades, you get to decide how much you want to apply. This is expressed as a factor, such as 2:1, 5:1, or 20:1. You then need to multiply your ‘margin’ by the factor to determine how much your trade is actually worth.
Leverage can be a difficult battleground to understand at first glance, so we’ve provided a simple example below.
Example of Using Leverage When Trading CFDs
Let’s say that you’re interested in trading the FTSE 100 – which represents the largest 100 companies listed on the London Stock Exchange (LSE). After the Brexit Referendum result was announced, the FTSE 100 took a major hit.
With that said, you felt that this was an overreaction from the markets and that the FTSE 100 would recover the following day. As such, you decided to trade the FTSE in the form of a CFD. However, you were super-confident on the trade, so you decided to apply leverage at 10:1.
Here’s how your trade would have worked in practice:
- You have £1,000 in your CFD brokerage account
- You apply leverage on the FTSE 100 at 10:1
- This means that you are trading £10,000 on the FTSE 100
- The price of the FTSE 100 increases by 5% the next day
- Ordinarily, your £1,000 trade would have yielded a profit of £50 (£1,000 x 5% )
- However, as you applied leverage of 10:1, you actually made a profit of £500 (£50 x 10)
As you can see from the above example, when a leveraged CFD trade goes in your favor, your profits can be amplified by some distance. However – regardless of your experience level, trades won’t always go your way. On the contrary, seasoned traders will always encounter losses.
Crucially, if the FTSE 100 had decreased by 5%, you would have lost £500. That is, of course, on the proviso that you failed to install sensible stop-losses. Don’t worry, we cover risk mitigation strategies in more detail further down.
How Much Leverage can I Apply to my CFD Trades?
As we noted in the above section, leverage trades are fraught with risk. This means that you could lose a lot of money if a CFD trade goes against you. As such, you will be limited in how much leverage you are able to apply to your CFD trades.
As such, for as long as the UK is a member of the European Union, you will need to follow the leverage limits imposed by the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) – which we’ve listed below.
- 30:1 for major forex pairs
- 20:1 for non-major forex pairs, gold, and major indices
- 10:1 for commodities other than gold and non-major equity indices
- 5:1 for individual stocks
- 2:1 for cryptocurrencies
However, the above limits are only in place for those that fall within the remit of a retail trader. If you’re a professional trader – and can satisfy the verification demands of the broker in question, ESMA limitations no longer apply. In some cases, this means that you can trade at leverage levels of up to 500:1.
AvaTrade - Established Broker With Commission-Free Trades

- Minimum deposit of just 250 USD to get lifetime access to all the VIP channels
- Awarded Best Global MT4 Forex Broker
- Pay 0% on all CFD instruments
- Thousands of CFD assets to trade
- Leverage facilities available
- Instantly deposit funds with a debit/credit card

Reducing the Risks of CFD Trading
Much like any other area of the online investment scene, you need to consider the risks of CFD trading. Crucially, if a trade doesn’t pan out as you had hoped, you’ll lose money. With that being said, there are a number of tools that you can utilize to reduce your overall exposure to a losing CFD trade. At the forefront of this is a stop-loss order.
✔️ Stop-Loss Orders
The most important tool that will reduce your chances of losing large amounts of money is a stop-loss order. In its most basic form, a stop-loss order allows you to exit a trade automatically when a certain price-point is triggered. For example, if you’re shorting gold, but the price increases sharply due to tensions in the Middle East, a stop-loss order can limit the amount that you lose.
Here’s an example of how stop-loss orders work in practice.
- You decide to go long on Bitcoin, meaning that you think the price will increase in the short-term
- You buy a Bitcoin CFD at $10,000
- Before you place your trade, you also install a stop-loss order
- You don’t want to lose more than 10% of your trade amount, so you put the stop-loss order in at $9,000
- Your Bitcoin trade goes against you, and the price is tanking. By the end of the day, Bitcoin has lost 20% and it is now valued at $8,000.
- However, you were able to exit the trade automatically at $9,000 – as per the stop-loss order that you installed.
Although stop-loss orders can be highly effective in reducing your overall exposure to a losing trade, they aren’t 100% fool-proof. On the contrary, in times of high volatility, the stop-loss order might not get executed. This is because the broker might be unable to match your order with another buyer on the platform. In such a scenario, your stop-loss order would not protect you.
However, the good news is that most CFD brokers active in the online space offer something called a ‘guarantee stop-loss order’. As the name suggests, this guarantees that your stop-loss order will be honored – regardless of whether or not the broker is able to find a buyer. In return for these guarantees, you will need to pay a higher trading fee, which is usually in the form of a wider spread.
How to Choose a CFD Broker?
So that you have a firm understanding of what a CFD is, how they work, and what risks you need to consider – we are now going to explore what you need to look out for when choosing a broker. Take note, no two brokers are the same, so you need to assess what’s important to you. For example, while some brokers specialize in super-low trading fees, others focus on the extensiveness of their trading platform.

Nevertheless, we would suggest evaluating the following factors prior to opening a new CFD broker account.
🥇 Regulation
The most important metric that you need to look at is whether or not the CFD broker is regulated. If you’re based in the UK, the broker will need to be authorized by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA).
If it isn’t, then the broker does not have the legal remit to operate. It is also notable if the CFD broker holds licenses in other jurisdictions.
🥇 Payments
You also need to consider how you intend to fund your CFD broker account. Most brokers will accept a debit or credit card, as well as a bank transfer. Some brokers even allow you to deposit funds via an e-wallet like PayPal and Skrill.
On top of the specific payment methods, you also need to look at deposit/withdrawal times.
🥇 Fees
Fees should also be at the top of your list when assessing whether or not a broker is right for you. We prefer CFD brokers that offer commission-free trading. Similarly, we also prefer brokers that offer tight spreads.
If you’re planning to trade on leverage, you also need to check the overnight financing fees that will be applicable.
🥇 Financial Instruments
When it comes to the trading arena itself, you need to explore what asset classes the CFD broker hosts. For example, if you prefer to trade stock market indices, check to see how many exchanges the broker lists.
The best CFD brokers typically offer thousands of financial instruments.
🥇 Trading Tools
If you’re looking to take your CFD trading endeavors to the next level, it’s crucial that you utilize charting tools. Such tools allow you to analyze historical pricing trends in an advanced manner, subsequently giving you the best chance possible of executing successful trades.
As such, choose a CFD broker that offers heaps of technical analysis tools.
🥇 Research
Whether you’re a newbie trader or a seasoned investor with years of experience under your belt – the utilization of research tools is a must. This is especially useful if you rely on fundamental analysis when placing CFD trades.
The best CFD brokers offer real-time news updates, analysis reports, and potential trading strategies on a particular asset.
CFD Trading: How do I get started? Step-by-Step Guide
Looking to get started with a CFD trading account today, but not too sure what you need to do? Check out the step-by-step guidelines that we have outlined below.
Step 1: Choose a CFD Broker
In order to start trading CFDs, you’ll need to use an online broker. There are literally hundreds of regulated CFD brokers active in the UK space, so the choice is plentiful. With that said, we would suggest reading the above section on ‘How to Choose a CFD Broker?’.
Once you’ve found a broker that meets your needs, move on to Step 2.
Step 2: Open an Account
You will now need to open an account with your chosen CFD broker. Firstly, you’ll need to enter some personal information. This will include your full name, home address, date of birth, national insurance number, and contact details. Make sure the information is correct, as you’ll need to verify it later.
You will also need to provide information about your financial standing. This should include your employment status, annual income, and whether you own or rent your home.
Step 3: Prior Trading Experience
In order to remain compliant with the FCA, UK CFD brokers must ensure that you have a firm understanding of the risks of trading. As such, you’ll be asked a range of questions regarding your prior trading experience – such as the types of assets you’ve previously invested in, and the average size of your trades.
You’ll also need to answer some multi-choice questions on the risks of leverage.
Step 4: Verify Your Identity (KYC)
Before you can deposit funds and begin trading, you will need to verify your identity. Once again, this is to ensure that the broker remains compliant with the FCA, as well as UK legislation on anti-money laundering.
Don’t worry, the verification process is super-easy, and merely requires you to upload some documents. In most cases, you’ll need to upload a copy of your passport or driver’s license, and a proof of address (such as a bank statement or utility bill).
Step 5: Deposit Funds
Once your identity has been verified. you can then fund your CFD broker account. Supported payment methods will vary from broker-to-broker, although this usually includes a bank transfer at a minimum. Credit and debit cards are also likely to be accepted. In some cases, the CFD broker might allow you to deposit funds via an e-wallet like PayPal.
Step 6: Start Trading
Congratulations – you’ve successfully opened a CFD brokerage account, verified your identity, and deposited funds! As a result, you are now ready to start trading. Take note, if you’re still a newbie in the CFD space, you are best advised to start trading with really small amounts.
Although some commentators will suggest using a demo account, this comes with its flaws. Crucially, demo accounts will not prepare you for the emotional side of losing money. As this is something that all traders will experience, it’s best to start your CFD career with micro-stakes.
1. AVATrade – 2 x $200 Forex Welcome Bonuses
The team at AVATrade are now offering a huge 20% forex bonus of up to $10,000. This means that you will need to deposit $50,000 to get the maximum bonus allocation. Take note, you'll need to deposit a minimum of $100 to get the bonus, and your account needs to be verified before the funds are credited. In terms of withdrawing the bonus out, you'll get $1 for every 0.1 lot that you trade.

- 20% welcome bonus of upto $10,000
- Minimum deposit $100
- Verify your account before the bonus is credited
2. VantageFX – Ultra-Low Spreads
VantageFX VFSC under Section 4 of the Financial Dealers Licensing Act that offers heaps of financial instruments. All in the form of CFDs - this covers shares, indices, and commodities.
Open and trade on a Vantage RAW ECN account to get some of the lowest spreads in the business. Trade on institutional-grade liquidity that is obtained directly from some of the top institutions in the world without any markup being added at our end. No longer the exclusive province of hedge funds, everyone now has access to this liquidity and tight spreads for as little as $0.
Some of the lowest spreads in the market may be found if you decide to open and trade on a Vantage RAW ECN account. Trade using institutional-grade liquidity that is sourced directly from some of the top institutions in the world with zero markup added. This level of liquidity and availability of thin spreads down to zero are no longer the exclusive purview of hedge funds.

- The Lowest Trading Costs
- Minimum deposit $50
- Leverage up to 500:1
CFD Trading Guide: Conclusion
If you’ve read our guide from start to finish, you should now have a really firm idea of what CFDs are, how they work, and what risks you need to consider. With the right risk-mitigation strategies in place, the CFD arena can facilitate most of your long-term investment goals. Whether you’re looking to gain exposure to stocks and shares, indices, interest rates, ETFs, or cryptocurrencies – CFDs allow you to buy and sell assets at the click of a button.
We have also provided guidance on the importance of choosing a CFD broker. With hundreds of platforms to choose from, you need to go with a broker that meets your individual needs. This might be a platform that supports PayPal deposits or a platform that charges super-low fees. Either way, just make sure that you perform due diligence on the CFD broker prior to opening an account.
FAQs
What does CFD stand for?
Spread betting v CFD - What's the difference?
What is the minimum deposit required at a CFD broker?
Who regulates CFD brokers in the UK?
What can I trade at a CFD broker?
What payment methods do CFD brokers accept?
Can I go short when I trade CFDs?