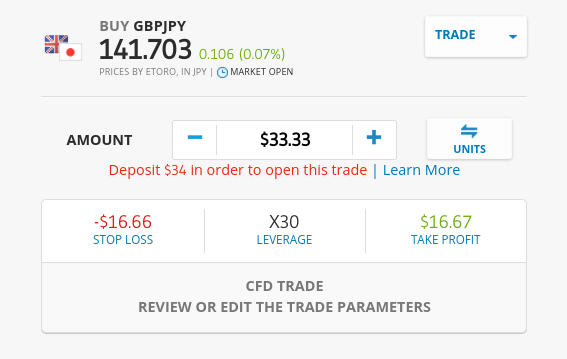
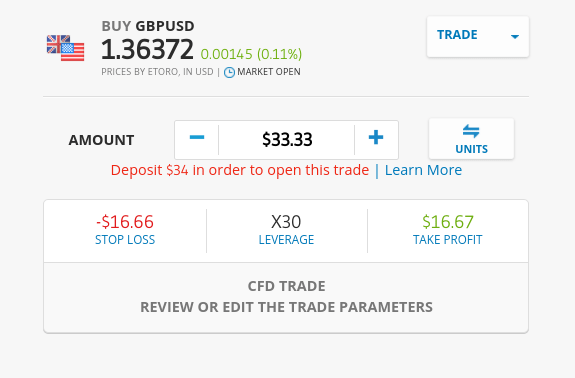
If you’re thinking about buying and selling currencies online – it’s crucial that you first learn how to trade forex. After all, in order to make money – you need to risk money.
Our Forex Signals
1 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
3 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
 Most popular
Most popular
6 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
Lifetime
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratioSeparate Swing Trading Group
 Up to 3 signals weekly
Up to 3 signals weekly 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiomonth
1 - month
Subscription
 Up to 15 signals daily
Up to 15 signals daily 76% success rate
76% success rate Entry, take profit & stop loss
Entry, take profit & stop loss Amount to risk per trade
Amount to risk per trade Risk reward ratio
Risk reward ratiotime
As such, you’ll need to have a firm grasp of how the forex markets work from top to bottom. Not only does this include an understanding of currency pairs, spreads, and market orders – but also research tools like technical indicators.
As you can imagine – there’s much to learn.
Fortunately, by reading this guide in full, you are going to learn how to trade forex from the comfort of your home. We walk you through everything you need to know so that you can get your forex trading career off on the right foot from day one!
Eightcap - Regulated Platform With Tight Spreads

- Minimum deposit of just 250 USD to get lifetime access to all the VIP channels
- Use our Secure and Encrypted Infrastructure
- Spreads from 0.0 pips on Raw Accounts
- Trade on the Award-Winning MT4 & MT5 Platforms
- Multi-jurisdictional Regulation
- No Commission Trading on Standard Accounts

Part 1: Understand the Basics of Forex Trading
In the first part of our Learn How to Trade Forex Guide, we are going to discuss the basics that every newbie trader needs to know. All in all, this information will sit at the core of your future forex trading career.
What is Forex Trading?
Put simply, ‘forex’ is the commonly used term to discuss the ‘foreign exchange’ of currencies. As you likely know, when you swap one currency to another, you will do so at a specific exchange rate. For example, if you’re based in the US and travel to the UK, you will be swapping US dollars for British pounds.

As a forex trader, your job is to speculate on whether the exchange rate of two currencies will go up or down at some point in the near future. After all, exchange rates will change on a second-by-second basis. For example, while you might get 1.37 dollars for each pound today, tomorrow you might only get 1.36.
With that being said – and as we cover in much more detail later on, forex exchange rates move in micro-units. For example, rather than displaying the exchange rate at 1.37 – your chosen forex broker might quote you 1.3760. This makes it highly conducive for day-to-day forex traders, as such a small movement in pricing facilitates plenty of opportunities to make money.
What Are Forex Pairs?
In the section above, we briefly discussed the exchange rate between the US dollar and the British pound. In this instance, the ‘pair’ is identified as GBP/USD. In Layman’s terms, a forex pair is simply the two currencies that you are speculating on.
In another example, if you were trading the Australian dollar against the Japanese yen, the pair in question is AUD/JPY. Once again, all forex pairs come with an exchange rate that changes on a second-by-second basis – so you need to predict whether this will increase or decrease in the short-term.
In total, there are over 100+ forex pairs that are commonly traded online. These pairs are typically split into three key categories – majors, minors, and exotics.
Major Forex Pairs
When you learn how to trade forex for the first time, you will usually be advised to stick with major pairs. As the name suggests, this is because these are the most liquid currency pairs that attract the largest volume. In turn, you will benefit from tighter spreads. Don’t worry, we cover these key terms in more detail later on.
Nevertheless, although major pairs always contain two strong currencies – one is always the US dollar. The other currency could be the Japanese yen, Australian dollar, Canadian dollar, or British pound.
Here’s a brief list of the most popular major forex pairs that you will find at your chosen broker:
| MAJOR PAIR | Nation of Currency |
| USD/JPY | United States / Japan |
| USD/CHF | United States/ Switzerland |
| AUD/USD | Australia / United States |
| USD/CAD | United States / Canada |
| GBP/USD | United Kingdom / United States |
| EUR/USD | Europe / United States |
| NZD/USD | New Zealand / United States |
Virtually all forex trading sites will give you access to the above major pairs.
Minor Forex Pairs
Minor forex pairs also contain two strong currencies – meaning they are heavily traded and attract heaps of liquidity. However, unlike majors, minor pairs do not contain the US dollar.
Here’s a brief list of the most popular minor forex pairs that you will find at your chosen broker:
| MINOR PAIR | Nation of Currency |
| GBP/JPY | United Kingdom / Japan |
| EUR/GBP | Europe / United Kingdom |
| EUR/CAD | Europe / Canada |
| NZD/JPY | New Zealand /Japan |
| EUR/NZD | Europe / New Zealand |
| CHF/JPY | Switzerland / Japan |
Much like majors, the best forex trading sites will cover most minor pairs.
Exotic Forex Pairs
The final forex pair category that you need to be aware of is that of exotics. These are pairs that contain a weak or emerging currency – such as the Thai baht or South African rand. Or, exotic pairs might contain a currency that comes from a strong economy.
But, the currency in question might be in low demand on a global scale. Think along the lines of the Norwegian krone or Hong Kong dollar. Either way – exotic pairs will also contain a strong currency, such as those found in major and minor pairs.
Here’s a brief list of the most popular major forex pairs that you will find at your chosen broker:
| EXOTIC PAIR | Nation of Currency |
| EUR/TRY | Europe / Turkey |
| USD/SEK | United States / Sweden |
| USD/DKK | United States / Denmark |
| EUR/ZAR | Europe / South Africa |
| GBP/HKD | United Kingdom / Hong Kong |
Now, if you are looking to learn how to trade forex in the best way possible, we would suggest sticking with majors and minors at first. The reason for this is that exotic pairs are a lot more volatile.
After all, they contain a currency that often comes from an emerging marketplace. As such, profits and losses can be a lot more parabolic. As exotic pairs also attract less liquidity, this means that the spreads are often a lot wider. Once again, we cover spreads in more detail later.
What are Forex Pips?
So far in our Learn How to Trade Forex Guide – we have covered the basics of majors, minors, and exotics. Next, we are going to explain how ‘pips’ work. In its most basic form – ‘Percentage in Points’, or simply pips, refers to the movement of a forex exchange rate in terms of units.
For example:
- Your forex broker is quoting 0.8899 on EUR/GBP
- A few seconds later, EUR/GBP is now being quoted at 0.8890
- This means that the pair has decreased by 9 pips.
In another example:
- Your forex broker is quoting 1.0772 on EUR/CHF
- A few seconds later, EUR/CHF is now being quoted at 1.0775
- This means that the pair has increased by 3 pips.
Crucially, when you trade forex online, you need to determine whether the exchange rate of the pair will increase or decrease. Your profit or loss will therefore not only be dictated by whether you speculated correctly, but how many pips you were right or wrong by.
Before moving on, it is important to note that pairs containing the Japanese yen are slightly different from others. While most brokers display 4 numbers after the decimal, yen-denominated pairs usually have just 2.
Quick Forex Trading Example
Before moving on to the next chapter of our How to Trade Forex Guide, it makes sense for us to give you a quick example of how a position might pan out.
- You want to trade the exchange rate between the Euro and the Canadian dollar. This is identified as CAD/JPY and it is a minor pair.
- The current price of the pair is 1.5504
- You think that the exchange rate will increase over the course of the day. As such, you place a buy order.
- A few hours later, CAD/JPY is priced at 1.5589
- This means that the pair has increased by 85 pips – so you’ve made a profit.
If, for example, you staked $1 per pip on the above forex trade, you would have made $85 (85 pips x $1). Similarly, if you had staked $5 per pip, your profit would have amounted to $425 (85 pips x $5).
Part 2: Learn Forex Orders
We are now at Part 2 of our ultimate guide on how to trade forex online. In this section, we are going to discuss the ins and outs of forex ‘orders’.
Put simply, you need to place an order so your chosen forex trading site knows what position you wish to take. This covers everything from whether you think the currency pair will increase or decrease in value, to the exact price that you want to enter the forex market.
Taking into account just how important forex orders are, we are now going to explain how each one works.
Buy Orders and Sell Orders
Irrespective of whether you trading forex, stocks, gold, oil, digital currencies, or ETFs – you will always need to start with a buy or sell order. In a nutshell, this determines whether you think the asset will increase or decrease in value. More specifically, whether the exchange rate of your chosen forex pair will rise or fall.
Here’s how it works:
- Do you think the forex pair will rise in value? If so, place a buy order.
- Do you think the forex pair will fall in value? If so, place a sell order.
It really is as simple as that!
However, it is also important to note that:
- If you enter your position with a buy order (meaning you think the pair will rise in value), then to close the trade – you’ll need to place a sell order.
- Similarly, if you enter with a sell order (meaning you think the pair will fall in value), then to close the trade – you’ll need to place a buy order.
In other words, each and every forex trade that you place will at some point contain both a buy and sell order.
Market Orders and Limits Orders
You now know that to enter a forex trade, you need to place either a buy or sell order. Once again, this lets your broker know which direction you think the market will go.
However, you also need to think about the specific price that you wish to enter the market. After all, forex exchange rates change every second, so you need to make sure that your trade is executed at the right time.
For this, your chosen forex broker will give you two options – a market order or a limit order.
Market Order
A market order is as simple as it gets, as you are instructing your forex broker to execute your trade instantly. This is useful if you spot a potential money-making opportunity and want to capitalize on it without delay.
However, as currency exchange rates change so rapidly, rarely will you get the exact price that you see on screen. On the contrary, there is likely to be a very slight difference.
For example:
- You are looking to place a buy order on GBP/JPY – which is currently priced at 141.46
- As a reminder, pairs containing the Japanese yen typically have just two numbers after the decimal point, as opposed to four.
- Nevertheless, you place a market order as you want to trade executed instantly
- A couple of seconds later, your trade is executed by the broker
- You check your order form and you entered the GBP/JPY trade at 141.47
As you can see from the example above, instead of 141.46, your trade was executed at 141.47. As such, the price difference is minuscule.
Limit Order
Make no mistake about it – the vast majority of seasoned forex pros will rarely opt for a market order. Instead, they much prefer limit orders. The reason for this is that limit orders give you 100% control over the price that you enter the market.
For example:
- You are looking to place a buy order on GBP/JPY – which is currently priced at 141.46
- However, you do not want to enter the market until GBP/JPY hits a price of 141.90
- This is because you think that the pair will go on a prolonged upward trajectory – should a price of 141.90 be breached.
- As such, you place a buy limit order at 141.90
Once you place your limit order, it will remain pending until your chosen entry price of 141.90 is triggered (or you manually cancel it). In other words, your order won’t be executed by the broker until this price is matched by the markets.
Stop-Loss Orders and Take-Profit Orders
So far, we have discussed buy and sell orders – which are required to enter the market. Then, we explored market and limit orders, which dictate the price in which your trade is executed.
As such, now it’s time to think about how you plan on closing your trade. Sure, we know that a sell order will close the trade if you entered with a buy order – and visa-verse.
However, seasoned traders will always have a specific exit strategy in place. This is based on a pre-defined price target and facilitated by stop-loss and take-profit orders.
Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders allow you to trade forex in a risk-averse manner. As such, all guides on how to trade forex should advise you to set up stop-loss orders on all positions – irrespective of how confident you are.
As the name implies, a stop-loss order allows you to exit a losing trade before things get out of hand. More specifically, you will let your broker know the exact price that you want the position closed automatically. Most forex traders base this on a percentage.
- For example, you might decide to go long on EUR/GBP – but you don’t want to risk more than 1% of your stake.
- In turn, you’d need to set up a stop-loss order that is 1% below your entry price.
- If, however, you were going short on EUR/GBP, your stop-loss order would be placed at 1% above your entry price.
Either way, your broker will ensure that your trade does not generate a loss of more than 1%.
Confused? Let’s elaborate on the above examples in a bit more detail:
- Once again, you are trading EUR/GBP. The pair is priced at 0.8899.
- If you were going long on the pair, this means that you think it will increase in value. To ensure you do not lose more than 1%, this means the stop-loss order should be placed at 0.8810
- On the other hand, if you were going short on the pair, the stop-loss order should be placed at 0.8987.
Crucially, placing a stop-loss order will ensure that you do not need to stare at your forex trading charts for hours-on-end. This will also alleviate sleepless nights where you are worried about waking up to significant losses.
On there contrary, you can rest soundly knowing that should things not go to plan – the most you can lose is 1% (or whatever percentage-based risk you are willing to take). As such, it is absolutely imperative that when you learn how to trade forex for the first time – you understand the importance of deploying stop-loss orders on all positions.
Take-Loss Orders
At this stage of the order placement process, you have the following factors in play:
- A buy or sell order – based on whether you think the forex pair will rise or fall
- A market or limit order – based on whether you to execute the trade immediately or at a specific price
- A stop-loss order – based on the maximum amount that you are prepared to lose on the trade
Taking the above into account, there is just one more metric that needs to be considered – your profit target. Put simply, you should always go into a forex trade with a target in mind. If you don’t, how will you know when the time is right to cash in your gains?
This is where the take-profit order comes into play. Crucially, it works in exactly the same way the stop-loss orders we discussed above, but in reverse. That is to say, you can specify to your broker the exact price that you want your forex trade close – based on a percentage-based profit target.
Let’s clear the mist with a quick example:
- Your buy order on EUR/GBP was executed at a limit order price of 0.8895
- You want to make 3% on this trade. This means that you need the price of EUR/GBP to increase by 3%.
- As such, you set up a take-profit order at a price of 0.9161
Ultimately, if the price of EUR/GBP does increase to 0.9161, your forex broker will close the trade automatically and you will have locked in a profit of 3%.
Part 3: Learn Forex Risk-Management
If you’re planning to enter the forex market for the first time without a sensible risk-management plan in place – forget about it. This is because you’ll simply end up blowing through your trading capital once you go on a prolonged losing run.
After all, even the most seasoned forex traders will at some point have a losing week or month. To ensure these losses do not have a devastating impact, experienced traders will follow their risk-management strategy to the “t”.
To help you along the way, this section of our Learn How to Trade Forex Guide will discuss some of the most effective risk-management strategies to consider.
Percentage-Based Forex Bankroll Management
First and foremost, it is absolutely imperative that you deploy a bankroll management system that is percentage-based. In Layman’s terms, this is the maximum amount of money that you will risk on a single forex trade – in relation to how much you have in your trading account.
In most cases, the “Magic Number” that seasoned forex pros implement is 1%. That is to say, the trader will never stake more than 1% of the available capital held in their brokerage account. For example, if you have a balance of $2,000, a 1% rule will permit a maximum stake of $20.
However, it goes without saying that after each and every forex trade you place, your balance will go up or down – depending on whether it’s a winner or loser. In turn, this means that the size of your maximum stake will also change.
For example:
- Your balance is $10,000, so at 1%, you cannot stake more than $100
- 1 week has passed, and your balance now stands at $13,000. As such, the 1% rule permits a maximum stake of $130
- You then go on a prolonged losing run, and your balance is now at just $8,500. As such, the maximum stake permitted is now $85.
The main concept with a bankroll management strategy is that your stakes will always fall in-line with the success or failure of your forex trading endeavors. In other words, the more successful you get, the larger you can stake. However, when trades start going against you, the size of your stake will decline. All in all, this ensures that you will never burn your entire bankroll.
Forex Trading Risk and Reward Ratio
The risk and reward ratio dictates how much profit we seek to make and how much risk we are prepared to take to get it. The easiest way to quantify this is again through a percentage-based system.
For example, you might deploy a strategy that seeks to make a 4.5% profit on each trade. At the same time, you are only prepared to risk 1.5%. This means that your risk/reward ratio stands at 1:3.
Although you don’t need to stick to your proposed risk/reward strategy religiously, this will keep you in check at all times. After all, you will have a systematic profit target and maximum loss framework in place – which you can facilitate via a take-profit and stop-loss order.
Forex Leverage
Leverage is both a risk and a potential reward. For those unaware, leverage allows you to trade with more money than you have in your brokerage account. In fact, this is something offered by the vast majority of currency trading sites.
While some platforms display leverage as a ratio (e.g. 1:10), others do so as a multiple (e.g. 10x). Either way, the specific leverage dictates how much your forex stake is being amplified.
For example:
- You want to risk $500 from your trading account. You apply leverage of 1:30, meaning that the position is worth $15,000
- You want to risk $2,000 from your trading account. You apply leverage of 10x, meaning that the position is worth $20,000
In terms of how much leverage you should expect to be offered, this will depend on several factors. For example, if you’re based in the UK or Europe, then the most you can get from a regulated platform is 1:30 on major pairs and 1:20 on minors/exotics.
But, if you live in a country that does not have any specific leverage restrictions in place, it is not uncommon to come across platforms that offer as much as 1:1000. This means that a $200 account balance would allow you to enter a trade worth $200,000. In other words, you stand the chance to amplify your potential profits by a significant amount.
Let’s look at a quick example of what a leveraged position can do for a successful forex trade:
- You are trading GBP/USD. You place a buy order at 1.3250
- You stake $500 with leverage of 1:30
- A few hours later, GBP/USD is priced at 1.3376
- This means that you have made gains of 0.95%
- On a stake of $500, this would have made you a total profit of $4.75 – which is hardly enough to quit your day job!
- However, with leverage of 1:30 applied, your $4.75 profit translates into gains of $142.50
As you can see from the above, having access to leverage means that you can target sufficient daily gains even if you only have a small amount of capital at your disposal.
But, before you start counting your riches – there is a major drawback to applying leverage – liquidation. In simple terms, if your leveraged forex trade goes in the wrong direction by a certain percentage, your broker will close the trade and you will lose your stake.
In the example above, you applied leverage of 1:30 on a $500 stake. This means that on a trade worth $15,000 ($500 x 30), you only put up a margin of 3.33% ($500 of $15,000). In turn, if GBP/USD dropped in value by 3.33% – your trade would be liquidated and you would lose the entire $500.
Crucially, the higher the leverage amount applied, the more chance you have of being liquidated. This is why a sensible risk-management strategy will keep your leveraged trades in check.
Part 4: Learn How to Analyze Forex Prices
If you have read our guide on how to trade forex up to this point – you should now know the following:
- The basics of forex pairs and pips
- The many different types of forex orders
- How to deploy a risk-management plan
In this part of our guide, we are going to discuss the process of analyzing forex prices. After all, if you don’t have the capacity to perform some sort of analysis on a forex pair, how will you know whether to go long or short?
In this respect – there are two main drivers that you need to be aware of when it comes to the future direction of an exchange rate – fundamental analysis and technical analysis.
Fundamental Analysis in Forex
Fundamental analysis is a form of research that looks at real-world events. For example, if you were analyzing a stock, you would look at things like earnings reports and relevant news stories. In the world of forex, you will be more concerned with factors surrounding economic policy, interest rates, and political uncertainty.
In comparison to technical analysis – performing regular fundamental research is actually not too difficult. This is because it is relatively straightforward to determine whether a real-world event will have a positive or negative impact on the value of a currency.
For example:
- You read a news story about political unrest in Turkey
- This will, of course, have a negative impact on demand for the Turkish Lira
- In turn, you could capitalize on this by trading a pair like USD/TRY
- You are attempting to speculate on the Turkish lira going down in value, so you would need to place a sell order
In another example:
- It has just been announced that the US Federal Reserve is planning to print $1.7 trillion to help boost the domestic economy
- The creation of such much money subsequently results in the devaluation of the dollar
- In order to make money on this, it could be wise to place a buy order on GBP/USD
There are many other examples, albeit, the core principle remains the same. That is to say, fundamental analysis is a great way to help you speculate on which way an exchange rate is likely to move in the near future.
In conjunction with the guides and forex courses we have on this page, you can also brush up on your fundamental analysis skills by reading relevant books.
Technical Analysis in Forex
While the ins and outs of fundamental analysis can be picked relatively quickly, technical analysis is a whole different kettle of fish. For those unaware, technical analysis refers to the process of reading forex charts. For example, a chart of GBP/USD would show us the exact price action of the pair in question over a set period of time.
By analyzing charts, it is possible to find historical trends and how this relates to current prices. In doing to do this effectively, you will need to learn how to use forex indicators. These are tools that allow you to look for specific trends surrounding price action, volatility, market depth, and more.
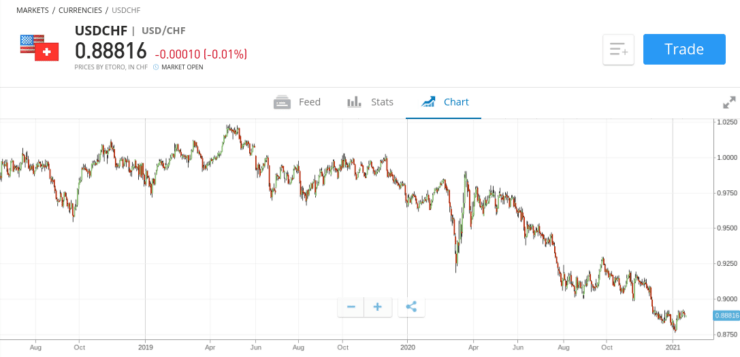
To help you along the way, there is a plethora of guides and articles on technical analysis here on our website. Externally, there are heaps of free videos on YouTube and of course – many books, too. However you decide to learn the ropes of technical analysis – this is something that cannot be avoided if you want to learn how to trade forex in the most effective way possible.
Forex Signals
We just mentioned how you won’t be able to trade forex without having a firm grasp of technical analysis. Although this is true to a certain extent, there is a slight workaround in the shape of forex signals. In a nutshell, forex signals are trading suggestions that tell you what orders to place.
This includes:
- Forex Pair
- Buy or Sell Order
- Limit Order Price
- Stop-Loss Price
- Take-Profit Price
The information itself is usually derived from an experience human trader that performs research on behalf of its members. Here at Learn 2 Trade, we have over 8,000+ members in our forex signals Telegram group. In most cases, our members receive 3-5 forex trading signals per day (Monday to Friday). We have a target success rate of over 70% and our traders typically implement of risk/reward ratio of 1:3.
If you want more information about how this works – check out our forex signals guide.
Part 5: Learn How to Choose a Forex Broker
It goes without saying that if you want to learn how to trade forex from the comfort of your home – you’ll need to find a suitable broker. After all, brokers are there to connect you to the financial markets. Each and every order that you place will be through the broker – so there are several key metrics that you need to check before opening an account.
To help point you in the right direction – below you will find a list of important factors to check-off in your search for a top-rated forex trading platform.
Regulation
Thinking about entrusting your trading capital with an unregulated platform? Forget about. Crucially, choosing a broker that is in possession of at least one license is really important.
In doing so, the broker in question will need to follow a set of regulatory rules – such as keeping your funds in a segregated bank account and collecting government-issued ID from all clients.
Regulated brokers are also required to have their books automated on a regular basis. This ensures that the broker is operating a transparent and fair trading platform for all.
Some of the most reputable financial bodies active in the brokerage scene include the FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia), MAS (Singapore), FINRA (US), and CySEC (Cyprus). The best forex sites will hold licenses from several of the above bodies.
Fees and Commissions
Every time you trade forex at your chosen broker, you will likely be charged a fee. In some cases, you will pay a ‘variable’ fee that is calculated against your stake.
For example, if your broker charges 0.2% and you place a leveraged order worth $5,000 – you will pay a commission of $10. Then, if you exit the position when it is worth $6,000 – your 0.2% commission will amount to $12.
Spreads
All online brokers charge a spread. This is an indirect fee that is calculated as the difference between the buy and sell price of your chosen forex pair.
For example:
- Let’s say that GBP/AUD has a buy price of 1.7850
- The same pair has a sell price of 1.7852
- This means that the spread in this example of 2 pips
If the spread on your chosen market is 2 pips, you need to make gains of 2 pips to break even. In other words, as soon as your trade is open, the spread results in you being 2 pips in red straight away.
In terms of what sort of spreads are competitive, this depends on what pricing model the broker takes. For example, if the broker is commission-free, then expect to pay a slightly higher spread. Similarly, if spreads are really competitive, then the commission might be on the high side.
Either way, always check this before signing up to a broker.
Tradable Forex Pairs
You also need to check what forex pairs your chosen broker offers. In a lot of cases, you will find that the vast majority of brokers offer all major pairs and most minor pairs.
When it comes to exotic pairs, this can be hit and miss. If you have a specific pair in mind, just make sure that the broker offers this. You can easily check this by visiting the website of the provider in question.
Payments
Don’t forget to check what payment methods the broker supports. It’s best to choose a platform that accepts instant payment methods like a debit or credit card.
E-wallets are also useful as they are fast, convenient, and usually fee-free. Additionally, check to see if any transaction fees are payable on your chosen payment method and how long the broker takes to execute withdrawal requests.
Best Brokers to Trade Forex Online
If you don’t have time to research dozens of brokers and instead want a bit of guidance, below you will find a selection of pre-vetted, regulated platforms that are worth considering.
1. eToro – Best Forex Broker for Beginners in 2023
If you are here reading this guide on how to trade forex, then it's likely that you are just starting out in the world of currency trading. If this is the case, then eToro is by far the best broker to consider. After all, the platform has clearly been designed for newbies in mind and so the forex department is really simple to navigate.
In fact, not only does it take minutes to get set up, but you can trade forex on the eToro account without needing to deposit any funds. Then, when you are ready to start trading with real money, you can instantly make a deposit with a debit/credit card or e-wallet.
In total, eToro offers over 50+ forex trading pairs. This offers a great blend of majors, minors, and exotics. You can also trade stocks, ETFs, indices, commodities, and cryptocurrencies - should any of these assets take your fancy.
Most importantly, you can trade forex at eToro commission-free and spreads are very competitive. What you will also like as a newbie is the eToro Copy Trading feature. This allows you to copy an experienced forex trader - meaning you will benefit from a passive investment experience.
Finally, and perhaps most importantly - eToro is a trusted broker that has been operational since 2007. It is now home to over 17 million clients and holds several regulatory licenses. This includes oversight from the FCA, CySEC, and ASIC.

- Heaps of forex pairs on offer
- Zero commission trading
- Great for beginners and super easy sign-up
- 0.5% conversion fee if not depositing in USD
2. EightCap – Best Commission-Free MT4 Broker
EightCap is another top-rated platform to trade forex. You'll have heaps of pairs to choose from - all of which can be traded commission-free with spreads starting at 1 pip. Or, you can opt for a 0 pip account that comes with a commission of $3.50 per slide.
EightCap is a great option if you are planning to trade with third-party platform MT4. This is because MT4 is compatible with forex robots that allow you to trade in a 100% passive nature. Additionally, MT4 is a good platform to learn the ins and outs of technical analysis.
In terms of safety, this popular broker is regulated by reputable body ASIC. You can easily open an account online or via the mobile app, with deposits starting at $100. And of course, Eightcap also offers demo accounts - so you can start off by trading risk-free.

- ASIC regulated broker
- Trade over 200+ assets commission-free
- Very tight spreads
- No cryptocurrency trading
Part 6: Learn How to Trade Forex Today – Walkthrough
If you have read our guide on how to trade forex all of the way through, we are going to conclude by getting you started with a trading account today. This includes the steps of registering with a broker, making a deposit, founding a market, and ultimately – placing your first-ever forex order.
Here’s what you need to do with user-friendly and commission-free platform eToro.
Step 1: Open an Account
Before you can trade forex at eToro, you need to head over to the provider’s website and open an account. For this, you will need to provide your personal information and contact details.
Step 2: Upload ID
eToro is regulated by several tier-one bodies, so it needs to collect a copy of your government-issued ID. This can be a passport or a valid driver’s license. You also need to provide a recently-issued utility bill or bank account statement.
You can add the above documents later and still make a deposit. But, you’ll need to do this before you can make a withdrawal (or attempt to deposit more than $2,250).
Step 3: Deposit Forex Trading Funds
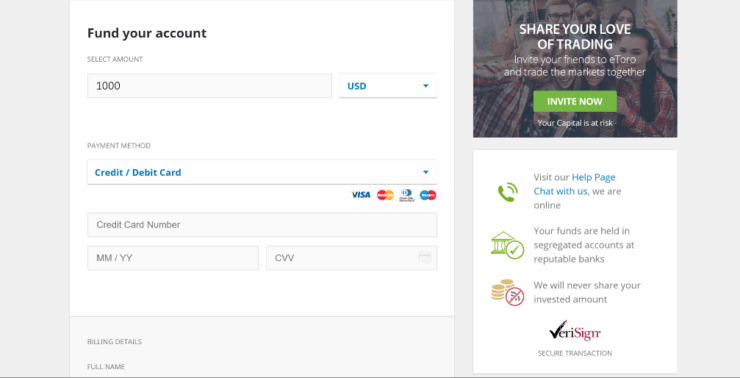
You will now need to add some funds to your forex trading account. This is instant at eToro when using a debit/credit card, Paypal, Neteller, or Skrill. If you want to perform a traditional bank transfer, this might take a few days to process.
Step 4: Start Trading Forex
You have now opened an account with eToro and made a deposit. Now all that is left is to place your first-ever forex order!
Before you do, we would suggest having a go on the eToro demo account facility until you find your feet. You test out all of the risk-management strategies that we discussed in this guide – as well as get to grips with orders and pricing charts.
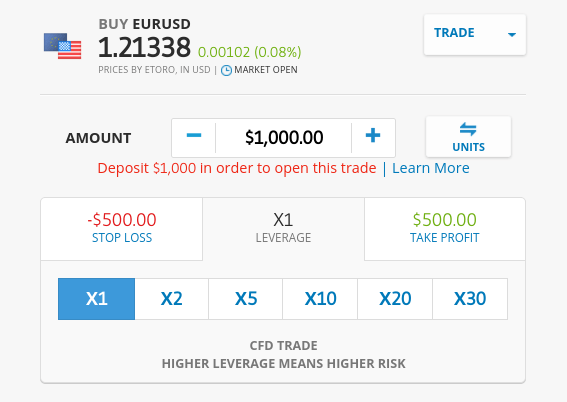
Finally, set up your orders – which will consist of a buy/sell order, market/limit order, stop-loss order, and a take-profit order. For a refresher on how each order type works, scroll up to the section “Part 2: Learn Forex Orders”.
Once you click on the ‘Open Trade’ button – your forex order will be placed!
Learn How to Trade Forex – The Verdict
By reading this comprehensive guide in full, you should now have a much better idea of how to trade forex from the comfort of your home. Although we have covered the basics, the forex trading learning journey has only just begun.
After all, you now need to go and learn the ins and outs of technical analysis and chart reading tools. In doing so, you’ll be able to make informed forex trading decisions without relying on help from a third-party.
All in all, just make sure that you keep your stakes to a minimum when starting your forex trading career and ensure you have a sensible risk-management strategy in place!
AvaTrade - Established Broker With Commission-Free Trades

- Minimum deposit of just 250 USD to get lifetime access to all the VIP channels
- Awarded Best Global MT4 Forex Broker
- Pay 0% on all CFD instruments
- Thousands of CFD assets to trade
- Leverage facilities available
- Instantly deposit funds with a debit/credit card